# Redux中间件
Redux 中一个简单的同步数据流动场景,点击 button 后,在回调中分发一个 action, reducer 收到 action 后,更新 state 并通知 view 重新渲染。
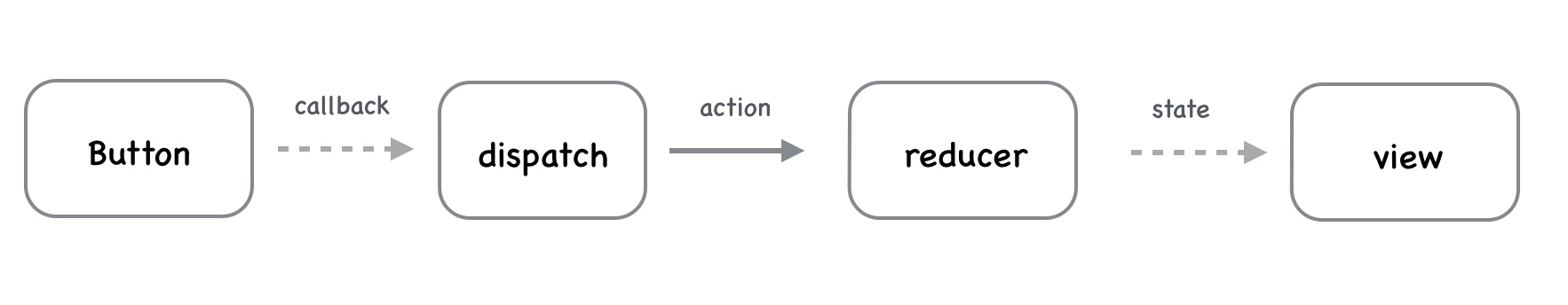 Redux同步数据流动
Redux同步数据流动
但是,如果需要打印每一个 action 信息来调试,就得去改 dispatch 或者 reducer 实现,使其具有 打印日志的功能。又比如,点击 button 后,需要先去服务端请求数据,只有等数据返回后,才能 重新渲染 view,此时我们希望 dispatch 或 reducer 拥有异步请求的功能。再比如,需要异步请求 数据返回后,打印一条日志,再请求数据,再打印日志,再渲染。
面对多样的业务场景,单纯地修改 dispatch 或 reducer 的代码显然不具有普适性,我们需要 的是可以组合的、自由插拔的插件机制,这一点 Redux 借鉴了 Koa里 middleware 的思想。另外,Redux 中 reducer 更关心的是数 据的转化逻辑,所以 middleware 就是为了增强 dispatch 而出现的。
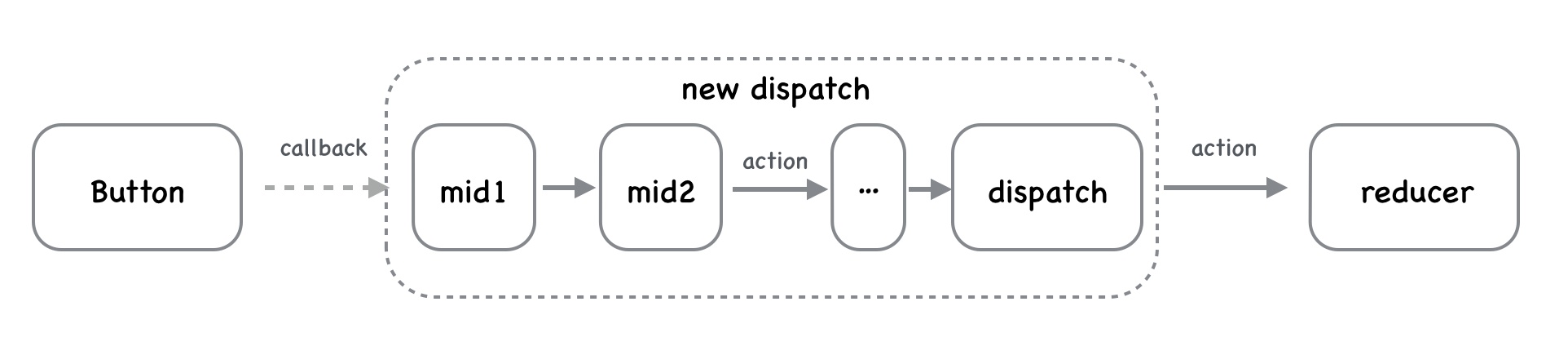
# 自定义redux中间件
redux中间一共嵌套了三层函数,分别传递了store、next、action这三个参数。
# applyMiddleware()
其实applyMiddleware就是Redux的一个原生方法,将所有中间件组成一个数组,依次执行。
//中间件多了可以当做参数依次传进去
const store = createStore(
reducers,
applyMiddleware(thunk, logger)
);
# 基本语法
import { createStore, applyMiddleware} from "redux";
const middleware = store => next => action {
//code....
next(action);
}
const store = createStore(
reducers,
applyMiddleware(middleware)
)
# 示例:日志中间件
import { createStore, applyMiddleware} from "redux";
//ES5
function logger(store) {
return function (next) {
return function (action) {
console.log('dispatching', action)
let result = next(action)
console.log('next state', store.getState())
return result
}
}
}
//ES6 箭头函数方式
const logger = store => next => action {
console.log('dispatching', action);
let result = next(action)
console.log('next state', store.getState());
return result;
}
const store = createStore(reducer,applyMiddleware(logger))
# 示例:错误处理中间件
import { createStore, applyMiddleware} from "redux";
const error = store => next => action {
try{
next(action);
}catch(err){
console.log("Error:",err)
}
}
const store = createStore(reducer,applyMiddleware(error))